What does RMM stand for?
RMM, short for remote monitoring and management, is a powerful tool to oversee and control computer systems or networks from a distance. This handy tool empowers administrators to take charge of network operations, requiring them to install software and supervise various activities.
RMM solutions boast a range of functions, but essentially, they help IT professionals achieve three primary objectives:
- Real-time monitoring and alerts: RMM solutions keep a constant watch on the health and performance of systems and networks, ensuring 24/7 surveillance. IT experts receive timely alerts about potential issues, allowing them to address concerns before they escalate. They can set up automated responses to these alerts and generate reports for comprehensive insights into network activity, asset inventory, compliance, and the overall value of IT support.
- Remote maintenance and remediation: Technicians leverage RMM software to carry out maintenance tasks and fix issues behind the scenes. They can deploy software, manage updates, execute scripts, and troubleshoot problems without disrupting end users' activities.
- Automating IT management tasks: RMM software streamlines workflows and automates various routine IT operations. From patch installations to script executions to ticket management, predetermined policies and actions ensure efficient handling of tasks.
Additionally, RMMs are commonly utilized to deploy and manage third-party endpoint security products and backup solutions.
Now, when you know how RMM works for businesses, it's no wonder that the majority of Managed Service Providers (MSPs) regard their RMM as their most critical application.
[Related article: Top 15 Endpoint Management Software]
You can also consider these top-rated CRM platforms to manage prospects and leads and strengthen relationships:
Here's a video with an overview of these CRMs to quickly familiarize yourself with the UI:
Evolution and history of RMM software tools
In the past, IT teams dealt with issues through the break/fix model. Whenever hardware or software malfunctioned, technicians had to physically go on-site to diagnose and fix the problem, often leading to lengthy resolution times. This model lacked consistent income for technicians as it operated without contracts or subscriptions, and customers didn't have ongoing support.
Then came the introduction of RMM software, revolutionizing how technicians managed IT assets. With RMM, technicians could monitor and manage systems remotely, shifting from reactive to proactive support. This software equips technicians with the necessary information and tools to perform preventive maintenance on users' IT assets, marking a significant improvement from the outdated break/fix approach.
[Related article: 24 Remote Work Tools & Software For Teams Working From Home In 2024]
What is RMM software used for?
RMM software plays a crucial role in the operations of an MSP business by allowing service providers to streamline operations and minimize labor costs effectively. By enabling remote management, MSPs can serve their clients efficiently, even without physically being on-site, thus reducing the time spent traveling between customer locations.
Furthermore, some RMM solutions offer automation capabilities, providing an added efficiency boost to enterprise IT systems. These tools come with prepackaged automation features such as check disk runs and script customization, allowing MSPs to proactively address IT infrastructure issues before clients even notice them. This proactive maintenance approach enhances customer satisfaction, as clients appreciate the proactive management of their systems.
What is RMM's strategy?
What is RMM software? RMM, or Remote Monitoring and Management, is a strategy used by IT service providers to remotely oversee and maintain clients' IT systems. It involves continuous monitoring, automated alerts, proactive maintenance, remote troubleshooting, security management, performance optimization, and reporting. The goal is to prevent downtime, enhance security, optimize performance, and reduce operational costs.
What is RMM in cyber security?
RMM in cybersecurity involves continuously monitoring endpoints, networks, and systems for security threats, vulnerabilities, and anomalous activities. It also includes tasks such as deploying security patches, updating antivirus software, managing firewalls, and responding to security incidents—all performed remotely to enhance the organization's security posture and minimize risks.
The #1 Rated RMM Option

4.8
NinjaOne's goal is to make life easier for IT providers.
It's on a mission to simplify your workdays, not complicate them. That's why it offers a modern solution that blends powerful features, user-friendly design, and unmatched support.
- Remote command line/PowerShell/terminal
- Task manager/activity monitor
- File Explorer / Finder
- Services manager
- Registry Editor
- Script deployment tool
- Performance thresholds (for example, CPU usage, storage utilization, etc.)
- Application, process, service, and daemon
- Device status
- Hardware changes
NinjaOne has been rated the best RMM software on G2 for four years in a row, thanks to its ease of use, IT management features, automation tools, secure remote access, and much more.
NinjaOne RMM enables users to get visibility and control over their IT infrastructures, provide proactive support, simplify technician workflows, and reduce expenses.
The key functions of remote monitoring and management software in IT management

Let's delve deeper into the daily IT tasks that RMM can assist you in completing for your clients:
- Gathering сlient information: RMM tools facilitate the collection of crucial data regarding client software, hardware, and network configurations.
- Providing activity reports: RMM solutions supply MSPs with comprehensive activity reports and data, offering insights into system performance and usage patterns.
- Alert generation and ticket creation: RMM software generates alerts and creates tickets automatically when issues arise, ensuring timely resolution and tracking of client concerns.
- Monitoring network and device health: RMM platforms continuously monitor the health and performance of networks and devices, allowing MSPs to identify and address potential issues proactively.
- Simultaneous endpoint and client monitoring: RMM tools enable MSPs to monitor multiple endpoints and clients simultaneously, ensuring comprehensive oversight across all managed systems.
- Automating maintenance tasks: RMM solutions automate scheduled maintenance tasks, such as software updates and system checks, reducing manual workload and ensuring system reliability.
By leveraging RMM for these tasks, your MSP team gains the freedom to focus on higher-level IT activities. With an ever-vigilant eye on system metrics via the RMM dashboard, you can deliver superior service to your clients. This newfound freedom also allows you to engage with your clients on strategic initiatives, providing valuable consultation on business growth and expansion opportunities.
[Related article: 15 Important Benefits of Remote Management and Monitoring]
Applicability of RMM tools in industries beyond IT
While Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools are primarily associated with the IT industry, their applicability extends beyond IT into various other industries. Here are some examples:
Manufacturing
RMM tools can be used to monitor and manage industrial equipment, machinery, and production processes remotely. This includes monitoring equipment performance, detecting malfunctions or deviations from normal operation, scheduling maintenance tasks, and optimizing production efficiency.
Healthcare
In healthcare, RMM tools can monitor medical devices, patient vital signs, and healthcare facilities remotely. This allows healthcare providers to ensure patient safety, track medical equipment usage, and respond quickly to any abnormalities or emergencies.
Utilities
RMM tools can be applied in the utilities sector to remotely monitor and manage infrastructure such as power plants, water treatment facilities, and distribution networks. This enables utility companies to optimize resource utilization, detect and respond to equipment failures or leaks, and ensure continuous service delivery.
Transportation
RMM tools can be used to monitor and manage fleets of vehicles, aircraft, or maritime vessels. This includes tracking vehicle performance, fuel consumption, route optimization, and scheduling maintenance tasks to ensure safe and efficient transportation operations.
Telecommunications
Telecommunications companies can use RMM tools to monitor and manage network infrastructure, including routers, switches, and communication towers.
Facility Management
RMM tools can be applied in facility management to remotely monitor and manage building systems such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), security systems, lighting, and energy consumption. This enables facility managers to optimize energy efficiency, detect equipment failures or security breaches, and ensure a safe and comfortable environment for occupants.
How RMM tools empower small and medium-sized businesses
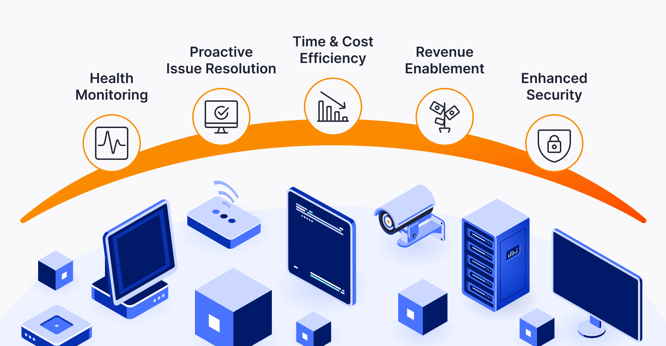
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools empower small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) in several ways:
Cost-Effective IT Management
SMBs often have limited IT resources and budgets. RMM software allows them to efficiently manage their IT infrastructure remotely, reducing the need for onsite IT support and minimizing operational costs.
Proactive Issue Resolution
RMM tools enable SMBs to proactively monitor their IT systems for potential issues, such as software failures, security vulnerabilities, or hardware malfunctions. By identifying and addressing these issues before they escalate, SMBs can minimize downtime and maintain productivity.
Enhanced Security
Cybersecurity threats are a significant concern for SMBs. RMM platforms help SMBs strengthen their security posture by continuously monitoring for security threats, applying patches and updates, managing firewall configurations, and enforcing security policies.
Remote Access and Support
With RMM tools, SMBs can remotely access and support their employees' devices and systems. This capability streamlines troubleshooting and support processes, reducing the need for onsite visits and minimizing disruptions for employees.
Improved Compliance
Many SMBs operate in regulated industries with compliance requirements related to data protection and privacy. RMM programs help SMBs ensure compliance by monitoring and managing IT systems according to regulatory standards and requirements.
Increased Productivity
By automating routine IT management tasks and providing proactive monitoring and support, RMM tools help SMBs maximize productivity. Employees can focus on their core responsibilities without being hindered by IT-related issues or disruptions.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
RMM solutions often include features for data backup and disaster recovery, helping SMBs protect their critical data against loss or corruption.
[Related article: Top 10 CRMs For Small Businesses]
What is the difference between MDM and RMM?
Here's a comparison table highlighting the key differences between Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM):
| Criteria |
Mobile Device Management (MDM) |
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) |
| Primary Focus |
Managing and securing mobile devices (smartphones, tablets, etc.) |
Managing and monitoring IT infrastructure (servers, endpoints, etc.) |
| Key Features |
|
|
| Device Types Supported |
Mainly mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops |
Various IT assets including servers, workstations, routers, etc. |
| Industry Applications |
Commonly used in organizations with a mobile workforce or BYOD policies |
Widely used in IT service providers, enterprises, and SMBs |
What is an RMM and MDM? While MDM focuses on managing and securing mobile devices, RMM is more comprehensive, covering a broader range of IT infrastructure assets such as servers, workstations, and network devices.
The benefits of using remote monitoring and management tools
What are RMM tools? Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools are expected to assist Managed Service Providers (MSPs) in handling the day-to-day operational tasks of their clients' networks. There are several advantages that arise when these tools are effectively utilized by MSP technicians.
Real-time monitoring
RMM enables real-time surveillance, giving small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) access to sophisticated automation and monitoring capabilities typically found in larger enterprises.
Proactive issue detection
By proactively identifying potential issues, RMM helps prevent crises or major system breakdowns. With its reporting features, the software can promptly alert MSPs to emergencies and issues as they occur.
Automation and scripting
RMM tools offer automation and scripting capabilities, enabling MSPs to streamline repetitive tasks and workflows. This not only increases operational efficiency but also reduces manual intervention, freeing up technicians to focus on more strategic tasks.
Performance monitoring
RMM facilitates continuous performance monitoring of clients' systems. This means MSPs can monitor endpoints in real-time, allowing them to promptly notify clients of any issues or opportunities for performance enhancement.
Cost savings
Through automation, proactive issue detection, and performance optimization, RMM helps MSPs save costs in several ways. By preventing costly downtime, minimizing the need for onsite visits, and optimizing system performance, RMM contributes to overall cost reduction for both MSPs and their clients.
[Related article: Benefits of CRM for Small Business – It’s Important]
Evaluating RMM software: what to look for

When considering RMM options, it's crucial to evaluate them based on your specific needs and priorities. While many RMMs offer similar core features, their reliability and performance can vary. This highlights the importance of utilizing free trials to assess whether an RMM's strengths align with your top requirements.
Here are some essential feature requirements to look for in an RMM:
- Monitoring and alerting: A good remote monitor service should monitor not only workstations and servers but also SNMP devices like routers, switches, and printers. Cloud monitoring for application servers and websites should also be included, with real-time delivery of monitoring data and customizable alerting options.
- Remote management tool: Speed and reliability are crucial for remote access. Integration with third-party software like TeamViewer or Splashtop is common, while cloud-enabled RDP connections are also viable options.
- Patch management tool: An RMM should facilitate automated patching for both Windows and third-party applications, allowing scheduled updates during off hours to minimize disruptions.
- Reporting: The RMM should offer a wide range of reliable reports, including patch compliance, asset inventory, network performance, and executive summaries.
- Scripting: The ability to launch and schedule scripts with appropriate privileges is essential for automation and efficiency.
- Integrations: Integration with backup, remote access, endpoint security products, and Professional Services Automation (PSA) solutions is expected.
- Ease of setup: Some RMMs may require extensive implementation training and fees, while others are designed to be intuitive and reduce ramp-up time and costs.
- Ease of ongoing administration: Consider the time, effort, and expertise needed to manage the software beyond the licensing fee.
- Stability and reliability: Downtime with RMMs can be disruptive, so reliability is crucial for smooth operations.
- Customer support: Access to responsive and knowledgeable customer support can be essential for resolving issues promptly.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select remote monitor software that best fits your business needs and ensures efficient IT management for your clients.
[Related article: How to Choose a CRM System: Checklist with 6 Tips]
Is RMM software safe?
Remote desktop monitoring software can be safe if properly implemented and used. Key factors include robust security measures, regular updates, and strong access controls. Proper configuration, monitoring, and training are essential for maintaining security. Choosing a reputable vendor is also crucial. Despite its potential safety, ongoing vigilance and adherence to security best practices are necessary to mitigate risks.
How to choose the best remote monitoring management software for your needs

Choosing the best remote monitoring and management (RMM) software for your needs requires careful consideration of factors such as security features, scalability, ease of use, vendor reputation, and cost-effectiveness.
Define RMM software meaning for your company, assess your specific requirements, prioritize features that align with your goals, and evaluate multiple options before making a decision. By thoroughly researching and comparing RMM solutions, you can select the one that best meets your organization's needs and budget while providing reliable performance and security for managing your IT infrastructure effectively.